Potential or Voltage Transformer: The purpose of the Potential Transformer is to provide an isolated secondary voltage that is in-phase and exact proportionate representation of primary voltage.
Potential Transformers are used for both Protection and Metering purposes.
The topics covered in this post are
- PT-Windings
- PT-Name Plate Specifications
- PT-Secondary Winding Connecting methods
- PT-Practical Connection Scheme
Potential Transformer Windings:
Primary Winding:
Primary winding is connected between Phase and Neutral. The Neutral is solidly earthed.
Secondary Winding:
At least two secondary windings which are connected one in Star and other in Broken Delta.
Secondary winding neutral point is earthed to provide safety.

Potential Transformer-Name Plate Specifications:
1. Rated Primary Voltage:
It is the rated continuous thermal limit voltage.
2. Rated Secondary Voltage:
The rated secondary voltage usually 110/√3
3. Rated Burden:
PT is rated by maximum burden (VA) at which it remains within specified limits of error.
4. Insulation Level:
Combination of power frequency and impulse voltages at which PT can withstand.
5. Rated Voltage Factor:
The multiplying factor to be applied to the rated primary voltage to determine the maximum voltage at which a transformer must comply with the relevant thermal requirements for a specified time and with relevant accuracy requirements.

6. Accuracy Class:
A designation assigned to a voltage transformer, the errors of which remain within specified limits under prescribed conditions of use.
For measuring voltage transformers, the accuracy class is designated by the highest permissible percentage voltage error at rated voltage and with rated burden prescribed for the accuracy class concerned.
The standard accuracy classes for measuring voltage transformers shall be 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0 and 3.
Here 0.5 means ±0.5 percent voltage error and ±20” phase displacement.
The accuracy class for a protective voltage transformer is designated by the highest permissible percentage voltage error prescribed for the accuracy class concerned, from 5% of rated voltage to a voltage corresponding to the rated voltage factor.
The standard accuracy classes for protective voltage transformers are “3P” and “6P”.
Here 3P means ±3 percent voltage error and ±120” phase displacement.
Phase displacement means the difference in phase between the primary voltage and the secondary voltage vectors, the direction of the vectors being so chosen that the angle is zero for a perfect transformer. The phase displacement is said to be positive when the secondary voltage vector leads the primary voltage vector. It is usually expressed in minutes.
7. Rated Frequency:
The value of the frequency on which the requirements of this standard are based.
Potential Transformer Secondary Winding Connections:
PT Secondary winding has three types of connections.
- Star Connection:
Star winding is used for Metering and Protection Relays (Distance Relay, Directional Over Current Relay etc.)

- Open Delta Connection:
Open Delta or V connection formed with two phase PTs. Yellow phase is not there. It can’t be used for Ground fault measurement. For this type of connection possibility of ferroresonance is very low.
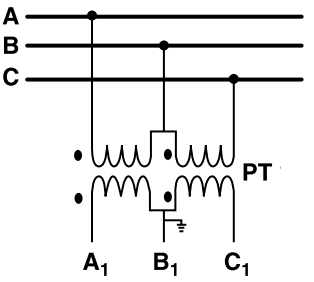
This connection is used for measurement of line voltages and phase matching between two source voltages.
- Broken Delta Connection:
It is formed by using three single phase PTs. For this type of connection all the secondary windings must be connected in series.

This connection is used to driving a Neutral Displacement Relay for detection of Earth fault in non-effectively earthed systems. Earth faults causes displacement of system neutral, particularly in the case of unearthed or impedance earthed systems.
Residual voltage is 3 times zero sequence voltage in case of Earth fault on primary side.
Ferroresonance may occur when applied broken delta connection on ungrounded or high impedance power systems.
Ferroresonance may be eliminated by using a single primary wye with dual secondary PTs where one PT secondary set is wye connected and the other PT secondary set is a broken delta as shown in figure.
What is Ferroresonance?
In electrical installations ferroresonances can occur if the following criteria are present:
• Use of single pole insulated voltage transformer
• The network is ungrounded (insulated neutral starpoint)
• Voltage surges caused by prior switching operations
In any of the above cases an oscillating circuit between the earth capacity (Ce) and the transformer inductance (Lw) will occur and reach a state of resonance. Hence saturation of iron core leads to overheating of the iron core as well as primary winding. Due to this Flashover of the high voltage to the grounded iron core and the secondary
winding will occur.
To avoid this damage the transformers can be equipped with a residual winding connected in broken delta circuit and equipped with a damping device (resistor, reactor or a combination of the two) as shown in below Figure. The design of this device depends on the thermal limiting output of the residual winding.
Practical PT Connections Arrangement:
The practical connection of single pole insulated voltage transformer with Star and Broken delta windings is shown in figure below.
In this connection shown, three phase supply given to 3 Single Pole PTs Primaries which are connected in star (shown by A, N which is the Primary winding of Single Pole PT) .

As shown in above figure 3 Single Pole PTs Secondaries connected in star (shown by a, n which is the first core of Single Pole PT) for providing voltages to Over Current relay and Voltmeter.
The broken delta connection (shown by da, dn winding which is the second core of Single Pole PT) is used to connect Earth fault relay.
PT Fuses:
H.R.C Fuses used on primary side. Primary side fuses protect the power system by de-energizing a failed P.T. Usually current limiting fuse is used in the primary connection to an ungrounded conductor.
PT MCB:
Fuses may not have sufficient interrupting capability so MCB is used.




very good and practical. to be more efficient if u focus protection core of Potential transformer
Can I use da-dn for measuring?
No, you should not use it. Here da-dn is meant for protection class Potential transformers only. If it is used for metering it will give inaccurate results.
How do you calculate the protection on the secondary side of the voltage transformer?
Hi,
I have a new PT, wye-wye connection, which has secondary side phases r-phase, b-phase and n connected to fuse, and y-phase connected to fuse link.
Any reason for this?
Thank you
Hi Alvin, This type of connection is an open delta connection as explained above. In this Y phase connected to ground via FUSE link.
Thanks for asking.
what will happen if broken delta connections are connected in parellel ? PT shall blast ?